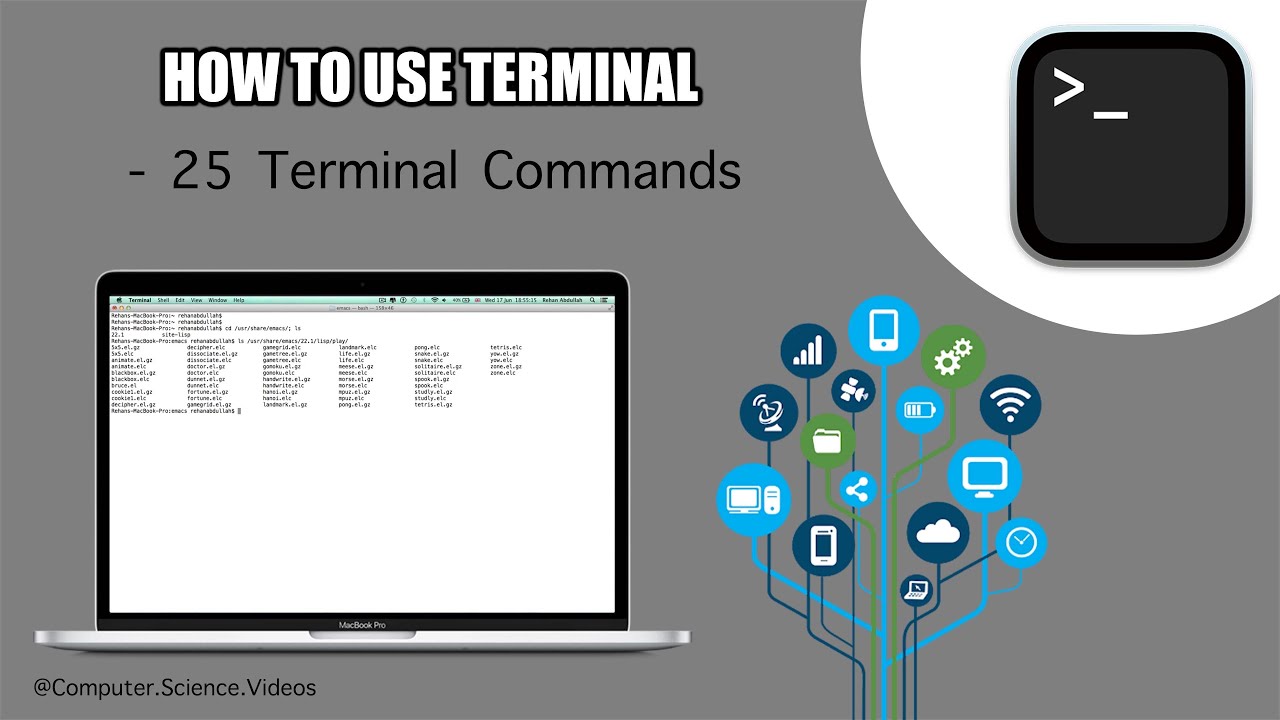
If you're working in Terminal on your Mac, you need to know the most important UNIX commands: those that work with directories, those that work with files, and miscellaneous but commonly used commands.
If you're working in Terminal on your Mac, you need to know the most important UNIX commands: those that work with directories, those that work with files, and miscellaneous but commonly used commands. Folders are called directories in UNIX. Commands that refer to filenames, as most do, assume that you're talking about files in the. Mac Terminal Commands List. There are tons of commands that you can make use of. Let's focus on some of the most common MacOS Terminal commands you need to be familiar with when you are mastering the Terminal. There are a few features that are applicable for any command. Terminal (officially called Terminal.app) is, strictly speaking, an emulator and works off most typical UNIX commands (OS X is a UNIX-based system, as opposed to Windows, which is NT-based). Unlike OS X, which has a graphical user interface (shortened to GUI), Terminal works off a text-based interface and all commands have to be typed in - this.
Folders are called directories in UNIX. Commands that refer to filenames, as most do, assume that you're talking about files in the working directory. When you open the Terminal window, the working directory is set to your home directory, abbreviated ~. Bash shows you the current working directory and your username to the left of its prompt. The following table lists common directory-related commands.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| ls | Lists the names of the files in the working directory. For more complete information, use ls –alF (. |
| cd directoryname | Changes the working directory to the one you named. |
| cd .. | Brings you up one directory level. |
| cd | Returns you to your home directory. |
| pwd | Displays the pathname of the current directory. |
| mkdir newdirectoryname | Makes a new directory. |
| rmdir directoryname | Removes (deletes) an empty directory. |
As in Windows, you can redirect the output of a command to a text file. So if you want a record of the files in a folder, type cd, followed by a space, drag the folder's icon to the Terminal window, and press Return. Type ls > mydirectorylist.txt and press Return again. A file named mydirectorylist.txt will appear in the folder you chose. You can open the file in TextEdit to see a list of the files in that directory.
This table lists commands commonly used when working with files in the Terminal window.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| cp filename1 filename2 | Copies a file. |
| chmod | Changes permissions for access to a file. Study the man page before using this one. |
| diff | Compares two files line by line (assumes text). |
| more filename | Displays a text file one page at a time. Press the spacebar to see the next page; press Q to quit. The man command works through more. |
| mv filename1 filename2 | Moves a file or changes its name. |
| rm filename | Removes (deletes) a file. |

This last table explains other handy commands that anyone getting started in Terminal will likely want to know.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Control+C | Terminates most operations. |
| date | Displays the current date and time. |
| echo | Repeats whatever appears after the command (after expansion). |
| help | Displays a partial list of bash commands. |
| history | Displays the last commands you typed. You can redo a command by typing an exclamation point (!) followed immediately (no space) by the number of that command in the history list. To repeat the last command, type !!. To repeat the last filename, type !*. |
| pico | A simple UNIX text editor. |
| ps | Displays a list of running processes. |
| sudo | Lets you carry out commands for which the account you are using lacks authority. You will be asked for an administrator's password. |
When you're working in Terminal, you don't have a Trash Can to which deleted files are moved pending ultimate disposal. Delete it, and it's gone. In general, UNIX has no Undo function.
Terminal User Guide
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| cp filename1 filename2 | Copies a file. |
| chmod | Changes permissions for access to a file. Study the man page before using this one. |
| diff | Compares two files line by line (assumes text). |
| more filename | Displays a text file one page at a time. Press the spacebar to see the next page; press Q to quit. The man command works through more. |
| mv filename1 filename2 | Moves a file or changes its name. |
| rm filename | Removes (deletes) a file. |
This last table explains other handy commands that anyone getting started in Terminal will likely want to know.
| Command | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Control+C | Terminates most operations. |
| date | Displays the current date and time. |
| echo | Repeats whatever appears after the command (after expansion). |
| help | Displays a partial list of bash commands. |
| history | Displays the last commands you typed. You can redo a command by typing an exclamation point (!) followed immediately (no space) by the number of that command in the history list. To repeat the last command, type !!. To repeat the last filename, type !*. |
| pico | A simple UNIX text editor. |
| ps | Displays a list of running processes. |
| sudo | Lets you carry out commands for which the account you are using lacks authority. You will be asked for an administrator's password. |
When you're working in Terminal, you don't have a Trash Can to which deleted files are moved pending ultimate disposal. Delete it, and it's gone. In general, UNIX has no Undo function.
Terminal User Guide
Use these shortcuts to save time when using Terminal.
Work with Terminal windows and tabs
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
New window | Command-N |
New window with same command | Control-Command-N |
New tab | Command-T |
New tab with same command | Control-Command-T |
Show or hide tab bar | Shift-Command-T |
Show all tabs or exit tab overview | Shift-Command-Backslash () |
New command | Shift-Command-N |
New remote connection | Shift-Command-K |
Show or hide Inspector | Command-I |
Edit title | Shift-Command-I |
Edit background color | Option-Command-I |
Make fonts bigger | Command-Plus (+) |
Make fonts smaller | Command-Minus (–) |
Next window | Command-Grave Accent (`) |
Previous window | Command-Shift-Tilde (~) |
Next Tab | Control-Tab |
Previous Tab | Control-Shift-Tab |
Split window into two panes | Command-D |
Close split pane | Shift-Command-D |
Close tab | Command-W |
Close window | Shift-Command-W |
Close other tabs | Option-Command-W |
Close all | Option-Shift-Command-W |
Scroll to top | Command-Home |
Scroll to bottom | Command-End |
Page up | Command-Page Up |
Page down | Command-Page Down |
Line up | Option-Command-Page Up |
Line down | Option-Command-Page Down |
Edit a command line
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Reposition the insertion point | Press and hold the Option key while moving the pointer to a new insertion point. |
Move the insertion point to the beginning of the line | Control-A |
Move the insertion point to the end of the line | Control-E |
Move the insertion point forward one character | Right Arrow |
Move the insertion point backward one character | Left Arrow |
Move the insertion point forward one word | Option-Right Arrow |
Move the insertion point backward one word | Option-Left Arrow |
Delete to the beginning of the line | Control-U |
Delete to the end of the line | Control-K |
Delete forward to the end of the word | Option-D (available when Use Option as Meta key is selected) |
Delete backward to the beginning of the word | Control-W |
Delete one character | Delete |
Forward-delete one character | Forward Delete (or use Fn-Delete) |
Transpose two characters | Control-T |
All Commands For Mac Terminal Download
Select and find text in a Terminal window
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Select a complete file path | Press and hold the Shift and Command keys and double-click the path |
Select a complete line of text | Triple-click the line |
Select a word | Double-click the word |
Select a URL | Press and hold the Shift and Command keys and double-click the URL |
Select a rectangular block | Press and hold the Option key and drag to select text |
Cut | Command-X |
Copy | Command-C |
Copy without background color | Control-Shift-Command-C |
Copy plain text | Option-Shift-Command-C |
Paste | Command-V |
Paste the selection | Shift-Command-V |
Paste escaped text | Control-Command-V |
Paste escaped selection | Control-Shift-Command-V |
Find | Command-F |
Find next | Command-G |
Find previous | Command-Shift-G |
Find using the selected text | Command-E |
Jump to the selected text | Command-J |
Select all | Command-A |
Open the character viewer | Control-Command-Space |
Mac Os Terminal Commands List
Work with marks and bookmarks
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Mark | Command-U |
Mark as bookmark | Option-Command-U |
Unmark | Shift-Command-U |
Mark line and send return | Command-Return |
Send return without marking | Shift-Command-Return |
Insert bookmark | Shift-Command-M |
Insert bookmark with name | Option-Shift-Command-M |
Jump to previous mark | Command-Up Arrow |
Jump to next mark | Command-Down Arrow |
Jump to previous bookmark | Option-Command-Up Arrow |
Jump to next bookmark | Option-Command-Down Arrow |
Clear to previous mark | Command-L |
Clear to previous bookmark | Option-Command-L |
Clear to start | Command-K |
Select between marks | Shift-Command-A |
Other shortcuts
Action | Shortcut |
|---|---|
Enter or exit full screen | Control-Command-F |
Show or hide colors | Shift-Command-C |
Open Terminal preferences | Command-Comma (,) |
Break | Typing Command-Period (.) is equivalent to entering Control-C on the command line |
Command-P | |
Soft reset terminal emulator state | Option-Command-R |
Hard reset terminal emulator state | Control-Option-Command-R |
Open a URL | Hold down the Command key and double-click the URL |
Add the complete path to a file | Drag the file from the Finder into the Terminal window |
Export text as | Command-S |
Export selected text as | Shift-Command-S |
Reverse search command history | Control-R |
Toggle 'Allow Mouse Reporting' option | Command-R |
Toggle 'Use Option as Meta Key' option | Command-Option-O |
Show alternate screen | Option-Command-Page Down |
Hide alternate screen | Option-Command-Page Up |
Open man page for selection | Control-Shift-Command-Question Mark (?) |
Search man page index for selection | Control-Option-Command-Slash (/) |
Complete directory or file name | On a command line, type one or more characters, then press Tab |
Display a list of possible directory or file name completions | On a command line, type one or more characters, then press Tab twice |
